Corrosion
Corrosion is an electrochemical reaction that degrades metallic materials and it is a big problem for many industries. The cause of corrosion failures can be determined by identifying the type of corrosion occurring and analyzing the deposits formed. Common types of corrosion are pitting, crevice corrosion, environmentally induced cracking (EIC) such as hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), microbiologically-induced corrosion (MIC), corrosion fatigue cracking (CFC), stress-corrosion cracking (SCC), and galvanic corrosion.
Analyzing Corrosion
Causes of Corrion and Corrosion Types
corrosion occurs due to the characteristics of materials and the environment. Houston Electron Microscopy can analyse the material and determine the material's composition and detect characteristis that are not seen with the naked eye along with the morphology and element composition. Corrosion, especially in metals, can manifest in various ways. The eight forms of corrosion are widely recognized in the field of corrosion engineering and science to categorize the different mechanisms through which metals deteriorate in specific environments. These are:

Corroded Metal

EDS Element Mapping - Iron-Oxide
Uniform Corrosion Attack
This is the most common type of corrosion and occurs evenly across the surface of a material. It typically results in a gradual thinning of the material. The SEM/EDS analysis shows Iron-oxide.
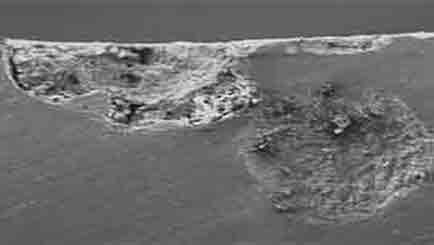
Low Magnification of Pitting

SEM/EDS Element Mapping - Iron Chrodie
Pitting
Pitting corrosion creates small, localized holes or pits on the surface of a material. It can be challenging to detect and often occurs in areas with oxygen depletion.

Example of galvanic corrosion
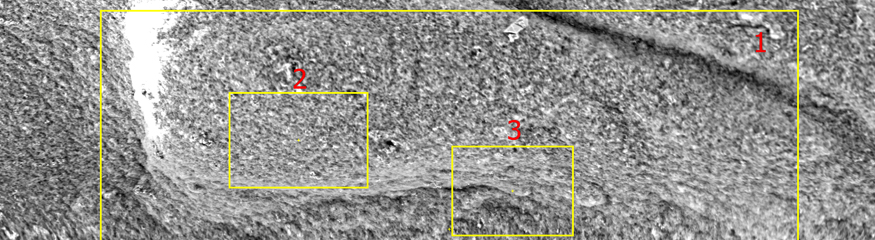
SEM micrograph of the residual solids from water sample – 2000X. Untreated segment of pipe in the system resulted in galvanic corrosion.
Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals come into contact in the presence of an electrolyte (e.g., saltwater), leading to one metal corroding faster than the other.

Notice corrocion at crevice site
Aluminum oxide/hydroxide corrosion deposit on.
Crevice Corrosion
Crevice corrosion happens in confined spaces or crevices where moisture and oxygen can accumulate. It is typically more severe than uniform corrosion.

Exfoliation is a form of intergranular corrosion

Intergranular corrosion
Intergranular Corrosion
Intergranular corrosion occurs along the grain boundaries of a material. It is often the result of impurities or sensitization of the material.

Characteristic SEM image of SCC
Root crack can be found with the help of the SEM
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC)
SCC is a form of corrosion that results from the combined effects of tensile stress and a corrosive environment. It leads to the formation of cracks.

Root crack can be found with the help of the SEM

Root crack can be found with the help of the SEM
Errosion Corrosion
Erosion corrosion occurs when the surface of a material is worn away by the abrasive action of fluids containing particles or impurities.

MIC may be a problem in deep sea drilling

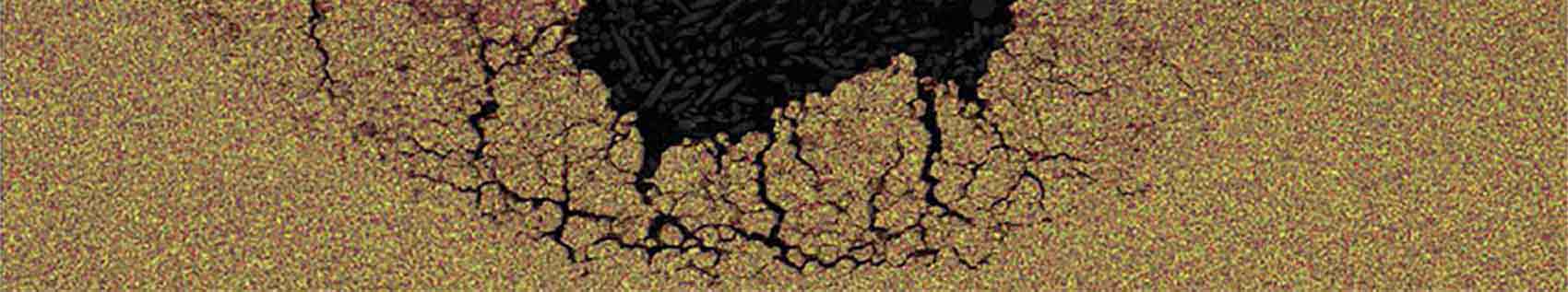
Bacteria can be seen in corroded metal, SEM 5K
Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC)
MIC is caused by the presence and activities of microorganisms such as bacteria, algae, or fungi that produce corrosive byproducts. MIC may occur in deep subsurface environments such as oil wells, processing facilities and hydrothermal vents.
Solutions to corrosion problems
Our mission is to deliver efficient, cost effective answers to your corrosion problems through SEM/EDS services, and micro FT-IR analysis. Same day or next day service can usually be scheduled. We want to help metallurgists, materials specialists, manufacturers, engineers, quality assurance managers, attorneys, and designers find solutions to material and quality problems.